Stereotaxis (NYSE: STXS) has announced a milestone in cardiac electrophysiology with the completion of the world’s first commercial procedures using its newly FDA-cleared Magic Sweep catheter. The landmark cases took place at Deborah Heart and Lung Center in Browns Mills, New Jersey, under the leadership of Dr. Raffaele Corbisiero and Dr. Pedram Kazemian.
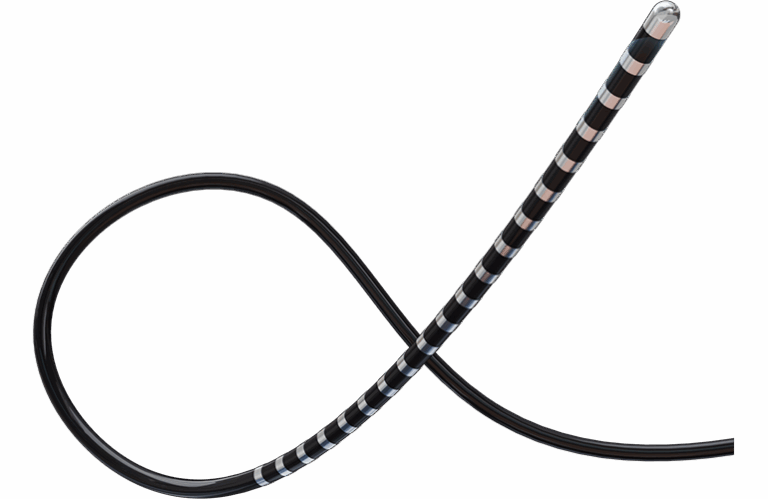
The Magic Sweep (MAGiC Sweep) catheter is a next-generation high-density (HD) electrophysiology mapping tooldesigned specifically for use with Stereotaxis’ Robotic Magnetic Navigation (RMN) systems. The technology allows clinicians to create high-resolution, anatomically precise maps of the heart, enabling more effective diagnosis and treatment of complex arrhythmias.
Stereotaxis received FDA clearance in July 2025 for Magic Sweep, and the successful completion of first-in-world commercial cases underscores its potential to redefine standards of precision in cardiac mapping and ablation procedures.
Clinical impact of high-density mapping
Cardiac electrophysiology is increasingly dependent on high-density mapping, which provides clinicians with greater detail and efficiency in identifying the sources of arrhythmias. By increasing both the volume and resolution of data points, HD mapping improves accuracy when locating abnormal electrical signals in the atria and ventricles.
“The ability to create a more accurate, detailed map of complex anatomy is important in diagnosing and treating arrhythmias. We have been impressed with the catheter during our experience mapping several different arrhythmias in the atria and ventricles,” said Dr. Corbisiero, chief of electrophysiology at Deborah Heart and Lung Center.
Magic Sweep incorporates 20 electrodes, facilitating rapid, detailed electroanatomical mapping while integrating seamlessly with Stereotaxis’ RMN systems. The catheter’s robotic compatibility allows for precise navigation into hard-to-reach areas of the heart, enhancing the physician’s ability to target arrhythmogenic tissue.
Design innovation and patient safety
Stereotaxis emphasized that patient safety was central to the catheter’s development. Magic Sweep features an atraumatic shaft designed to minimize the risk of cardiac tissue injury. Unlike rigid conventional catheters, its flexible design avoids chamber distension, which can distort anatomical accuracy during mapping.
This design not only improves the fidelity of cardiac maps but also optimizes workflows for robotic electrophysiologists. As Stereotaxis advances automation algorithms for mapping, Magic Sweep’s compatibility is expected to support automated, real-time mapping, making procedures faster and more efficient.
Dr. Kazemian, who performed the inaugural cases with Dr. Corbisiero, highlighted the significance of the innovation:
“This is a significant leap forward for the community of robotic electrophysiologists and we look forward to the positive impact its expanded use will have on our patients and the EP field.”
Why robotic mapping matters
The introduction of Magic Sweep advances the use of robotic magnetic navigation systems in electrophysiology. RMN technology already enables remote-controlled catheter navigation, reducing physician fatigue, lowering radiation exposure, and enhancing precision in complex procedures. By adding a robotic-compatible HD mapping tool, Stereotaxis is closing the gap between traditional manual catheter systems and the advantages of robotics.
For physicians, this means more confidence in procedural accuracy; for patients, it offers the potential for shorter procedure times, fewer complications, and improved outcomes.
Strategic milestone for Stereotaxis
The successful commercial adoption of Magic Sweep is not just a technological achievement—it’s a strategic one. Stereotaxis has long positioned itself as a pioneer in robotic electrophysiology, and the catheter approval extends its ecosystem of robotic-compatible solutions.
High-density mapping is becoming a clinical expectation in advanced electrophysiology labs. By delivering a catheter that combines HD mapping with robotic navigation, Stereotaxis strengthens its competitive edge in a market that increasingly values integration, efficiency, and safety.
The milestone also reflects broader momentum in electrophysiology, where pulsed field ablation (PFA), AI-driven mapping, and robotic solutions are converging to redefine standards of care. Stereotaxis’ ability to bring HD robotic mapping into commercial practice gives it a first-mover advantage in an area with significant growth potential.
Competitive dynamics in electrophysiology mapping and robotics
The commercial debut of Stereotaxis’ Magic Sweep catheter represents not only a technical milestone but also a competitive inflection point in the electrophysiology (EP) market, where major MedTech players are racing to combine mapping, ablation, and robotics into integrated platforms. By offering the first robotic-compatible high-density (HD) mapping catheter, Stereotaxis enters a high-stakes contest against global leaders like Johnson & Johnson’s Biosense Webster, Abbott, and Boston Scientific.
Mapping: the cornerstone of EP
Mapping is central to every ablation procedure, as physicians must first identify the arrhythmogenic substrate before delivering therapy. Historically, this domain has been dominated by:
Biosense Webster (Johnson & Johnson MedTech): The market leader with its CARTO mapping system, long considered the gold standard. CARTO integrates with multiple catheters, offering physicians flexibility but relying on manual catheter manipulation.
Abbott: Its EnSite X system provides detailed electroanatomical maps and has been positioned as a competitor to CARTO, emphasizing scalability and versatility.
Boston Scientific: With its Rhythmia HDx system, Boston Scientific has positioned itself around ultra-high-density mapping, offering operators very fine-grained electrical insights.
These systems have fueled remarkable advances in arrhythmia treatment. However, all three are primarily manual catheter-based platforms, which means the precision of the map still depends on the operator’s hand.
Stereotaxis’ Magic Sweep brings a different approach: robotically controlled HD mapping that can reach anatomically complex regions with greater precision and less operator variability. For physicians, this can reduce both procedure time and learning curve.
Robotics: Stereotaxis’ competitive edge
Unlike its larger rivals, Stereotaxis has built its brand identity entirely around robotic magnetic navigation (RMN). The system enables physicians to guide catheters using magnetic fields rather than manual manipulation, allowing for fine, consistent, and fatigue-free control.
By introducing an HD mapping catheter specifically designed for RMN, Stereotaxis strengthens its ecosystem and addresses one of the historical limitations of robotic systems: the lack of third-party catheter compatibility. Magic Sweep eliminates this barrier by giving robotic electrophysiologists a native HD mapping tool.
For hospitals already invested in Stereotaxis RMN systems, Magic Sweep enhances the value of their existing infrastructure. For those considering robotics, it makes adoption more attractive by removing the need to choose between mapping performance and robotic precision.
Strategic positioning against giants
The electrophysiology market is projected to exceed $15 billion globally by 2030, with ablation procedures growing steadily due to rising atrial fibrillation (AFib) prevalence. Within this space, mapping and navigation technologies are among the highest-value segments.
Biosense Webster maintains dominance through scale and entrenched clinical trust, but its strength lies in manual workflows.
Abbott leverages EnSite X’s flexibility but faces challenges in carving share away from CARTO.
Boston Scientific emphasizes density with Rhythmia but competes as a challenger in a crowded field.
Stereotaxis, though smaller in scale, differentiates by owning the robotic EP niche. Magic Sweep expands that niche into high-density mapping, allowing Stereotaxis to argue that it offers both safer, more precise navigation and equally advanced mapping capability.
If adoption accelerates, Stereotaxis could emerge as the go-to solution for high-volume centers seeking both cutting-edge mapping and the long-term safety benefits of robotics (reduced radiation exposure, reduced operator strain).
Market adoption drivers
The success of Magic Sweep will hinge on several adoption dynamics:
Clinical validation: Long-term data must demonstrate that robotic HD mapping leads to measurably better outcomes, including higher ablation success rates and reduced recurrence.
Workflow efficiency: Hospitals must see tangible improvements in case times and throughput compared to manual HD mapping systems.
Training and adoption: Robotic systems require a cultural shift. Widespread training programs will be necessary to expand the community of robotic electrophysiologists.
Economic justification: Hospitals must balance capital costs of robotic systems with the downstream benefits of improved efficiency, safety, and reduced repeat procedures.
The convergence of mapping, ablation, and automation
Magic Sweep also positions Stereotaxis for the next wave of EP innovation: automation. By integrating HD mapping with robotic navigation and developing AI-driven algorithms for automated mapping, the company is laying the foundation for semi-autonomous ablation procedures.
This vision—where robots handle repetitive tasks like mapping while physicians focus on clinical decision-making—could reshape workflows in the EP lab. Magic Sweep is the first step toward making robotic systems not just precise, but also smarter and more efficient.
Powered by Froala Editor